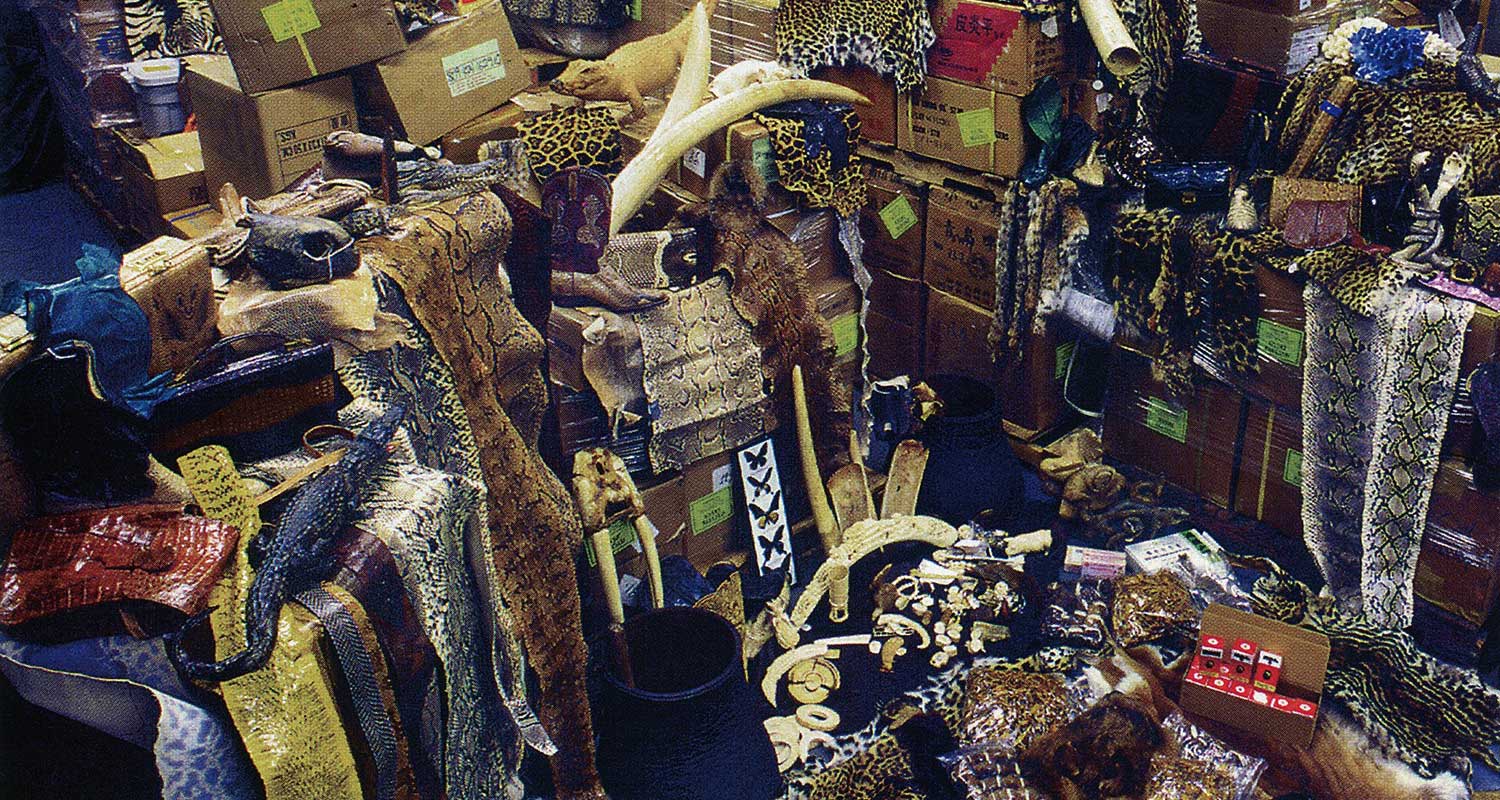
The alligator struggles to break free. But seven mighty blows to the back of its head abruptly end its futile attempts. Out cold, it receives another, but less brutal, coup de grace: a seven-centimetre incision on the spot where the deadly blows landed. Now slowly bleeding, it is left lying in a gutter. After more than one-and-a-half hours, the metre-long creature is dead. Its skin will be sold to make handbags for the fashion industry in Europe and North America. Clifford Warwick, a trustee of the Reptile Protection Trust, has watched several animals die this way. According to Warwick, alligators are simply skinned alive on a busy day in alligator farms, and survive like that for hours before dying. Documentary footage from Asian reptile farms also shows snakes and lizards being tortured for their prized skin. With meat hooks piercing their heads, they are disemboweled before their skins are pulled off. Dealers believe that the practice of skinning reptiles alive makes the skin more supple.
Other Uses For Reptiles
Aside from making fashion statements, reptiles also make popular ingredients for exotic dishes, traditional medicines and aphrodisiacs. There is an old Chinese belief that snake blood mixed with an alcoholic drink is an effective potion that increases sexual prowess.
In Vancouver’s Chinatown, fish vendors sell live soft-shelled turtles in bowls and chop them into pieces for soup. Christine Schramm of the Rainforest Reptile Refuge Society in Surrey, B.C., keeps a soft-shelled turtle that was rescued from the chopping block. Although she recognizes that different cultures eat different kinds of animals, the treatment of these wild animals seems particularly cruel. “They are slaughtered,” she says, “they are chopped up alive.”
Reptiles On The Black Market
The ever-increasing demand for reptiles as food is just one of the many factors that contributes to the growth of the reptile trade. The pet industry also plays a role in this increase as demand for rare species has driven prices upward, increasing the temptation to smuggle reptiles. “The illegal importation of or trade in exotic animals is third to weapons and drugs,” says Schramm. “It brings in millions of dollars every year, not only from the hides but also from the live animals for the pet industry.” For example, a Komodo dragon sells for $30,000 US on the black market while a Chinese alligator costs $15,000 US. Even the Philippines’ Gray’s monitor, a species that can be exported with a permit, commands a black market price of $8,000 US. These prices are way too high, even for a three-metre-long pet that can bite your face off.
Yet, collectors are still buying. “I don’t know what it is about reptiles,” continues Schramm, “some eight or nine-year-old kids who come in here say, ‘Wow, cool! Look at this! I’m gonna get one of these!’ I don’t know what the attraction is for them, but I think it’s our culture here in Canada and in the U.S. that we have to possess things. We have to control — it’s a control thing. It’s cool to have something captive in a cage.”
What Makes Us Want Reptiles In Our Homes?
But to Fabian Dawson, editorial consultant of the Southeast Asia Post, who wrote an article on the Asian reptile racket, it’s all about the allure of the exotic. “Who wants to have a snake at home? But then there are hundreds and hundreds of people around the world who seem to think that it’s good. Man is such a collector himself. The more rad a thing is, the more he wants to go out and get it.”
It’s our culture here in Canada and in the U.S. that we have to possess things. We have to control — it’s a control thing. It’s cool to have something captive in a cage.
Media and the entertainment industry are also partly to blame for the accelerated reptile trade, thanks to movies like Jurassic Park, The Lost World and Godzilla. These movies depict reptiles as aggressive, violent creatures, capable of destroying, maiming or killing. No ordinary, passive household pet can bite its prey, thrash it left and right, and swallow it whole. That’s why these modern-day dinosaurs are popular.
Illegal & Legal Trading Is On The Rise
In fact, these animals are so cool that the U.S., the dominant player in the reptile trade, imported 1.8 million live reptiles worth $7 million US and exported 9.7 million valued at more than $13.2 million US in 1997. This is only the legal stuff. The bulk of the trade is illicit, and millions of dollars worth of live reptiles are smuggled every year.
A case in point was the arrest of possibly the world’s biggest illegal reptile dealer and two of his cohorts in Mexico in September 1998. Authorities from Mexico, Canada and the U.S. found in their possession the following species: an Indonesian Komodo dragon, a rare New Zealand tuatara, exotic Madagascar tortoises, Chinese alligators, Southeast Asian false gavials and Philippine monitor lizards. Authorities are investigating how these creatures left their original habitats and landed in Mexico.
Legal or illegal, the reptile trade has raised conservation fears. “We need to step up research and take action to address fears that the trade is impacting some of the world’s wild reptile populations,” says Craig Hoover of TRAFFIC North America. In his report, The U.S. Role in the International Live Reptile Trade: Amazon Tree Boas to Zululand Dwarf Chameleons, he recommends several actions to help ensure that the booming trade is conducted in a manner that is beneficial to the world’s wild reptile populations. These include reviewing legislation and assessing effectiveness of implementation and enforcement for identified hot spots like Indonesia and Madagascar, where native reptile faunas continue to be threatened by trade. The recommendations also call for improvements in the implementation of CITES, the Convention on International Trade in
Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, which regulates international trade in animals and plants, and pursues trade bans. Yet animal rights lobbyists believe these recommendations aren’t enough to deter illegal traders. They clamour for stiffer penalties in a trade where the risk of being caught is relatively low – some even go so far as to suggest that authorities imprison offenders and throw away the key. Other reptile advocates propose that animals with scales and skin be provided the same dignity and respect afforded to those with fur or feathers.
However, no amount of lobbying and recommending is likely to impact the reptile trade as long as illegal animal dealers continue to disrespect borders. And two recent smuggling incidents since the big bust in Mexico serve as alarming reminders of this fact. The first case involved a Canadian and a Dutchman flying in from Thailand. Both were arrested at Chiang Kai-shek Airport trying to smuggle 303 endangered chameleons into Taiwan. In the second case, authorities found 1,000 cobras on their way out of Jakarta headed for Japan. Both cases happened within a span of less than two months. The trade is alive and slithering.